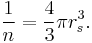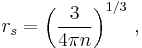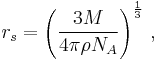Wigner–Seitz radius
The Wigner–Seitz radius 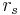 , named after Eugene Wigner and Frederick Seitz, is a parameter used frequently in condensed matter physics to describe the density of a system. The formula for 3-D system is
, named after Eugene Wigner and Frederick Seitz, is a parameter used frequently in condensed matter physics to describe the density of a system. The formula for 3-D system is
Solving for 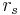 we obtain
we obtain
where  is the particle density of the valence electrons.
is the particle density of the valence electrons.
For a non-interacting system, the average separation between two particles will be 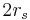 . The radius can also be calculated as
. The radius can also be calculated as
where  is molar mass,
is molar mass, 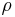 is mass density, and
is mass density, and 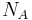 is the Avogadro number.
is the Avogadro number.
This parameter is normally reported in atomic units, i.e., in units of the Bohr radius.